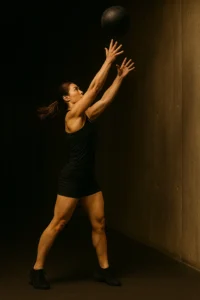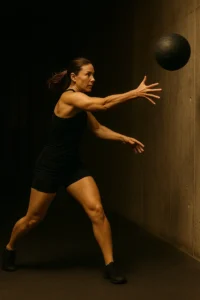Learn more about Med Ball Rotational Throw
Exercise Facts
Detailed How-To Med Ball Rotational Throw
The Med Ball Rotational Throw is a high-performance exercise that trains explosive rotational strength a key component in athletic power and real-world movement. It strengthens the obliques, hips, and shoulders while improving coordination between the lower and upper body.
To perform, stand side-on to a wall holding a medicine ball at chest height. Rotate your torso and hips away from the wall, then drive explosively toward it, releasing the ball with force. Catch or retrieve the rebound, reset, and repeat for the desired reps before switching sides.
This movement teaches how to generate power through rotation, making it ideal for athletes who sprint, swing, or throw. It also builds core stability and control through rapid deceleration, improving performance in both strength and conditioning programs.
Common mistakes include overusing the arms instead of rotating through the hips, or losing balance during the throw. Cue “load the hips,” “rotate from the ground,” and “snap through the core.”
In Relentless Bravery Fitness programming, 100 total throws (50 per side) are used to test rotational endurance, precision, and intent turning speed into skill.